- October 19, 2024
- Boat Maintenance
- Understanding Marine Diesel Engines
Marine diesel engines are the backbone of many vessels, from fishing boats to massive container ships. These powerful machines convert fuel into mechanical energy, enabling vessels to traverse oceans and navigate waterways. In this blog, we’ll delve into the workings of marine diesel engines, exploring their components, operation, and significance in the maritime industry.
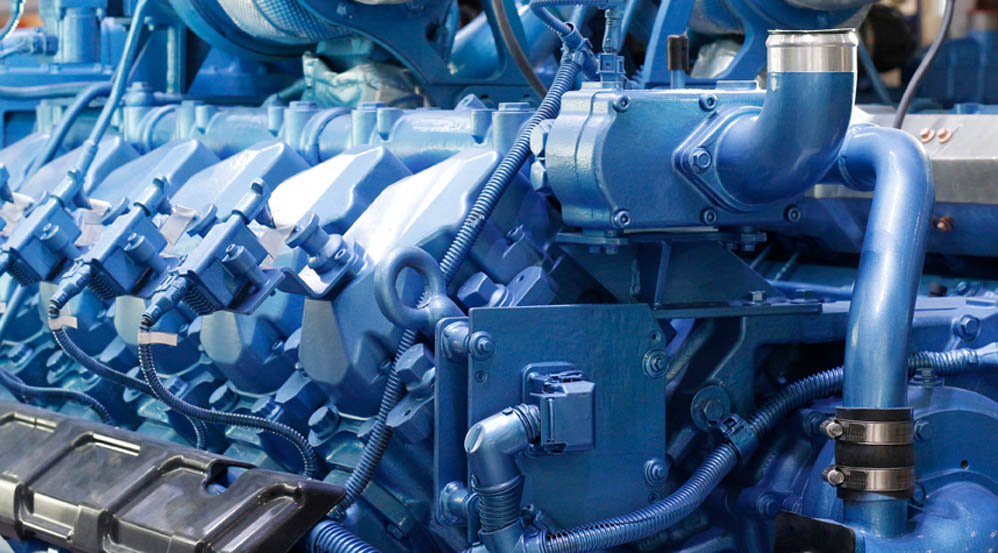
The Basics of Diesel Engines
Diesel engines operate on the principles of internal combustion, using diesel fuel to ignite air that has been compressed to high pressures. Unlike gasoline engines, which use spark plugs for ignition, diesel engines rely on the heat generated by compressing air to ignite the fuel. This difference in ignition methods makes diesel engines more efficient and durable, especially in marine applications.
Key Components of Marine Diesel Engines
- Cylinders: The core of the engine, where the fuel-air mixture is compressed and ignited. Most marine diesel engines have multiple cylinders, typically arranged in a line or a V configuration.
- Pistons: These move up and down within the cylinders, converting the pressure from combustion into mechanical energy.
- Crankshaft: The pistons are connected to the crankshaft, which converts linear motion into rotational motion, ultimately driving the propeller.
- Fuel System: This includes the fuel tank, filters, pumps, and injectors, which supply diesel fuel to the engine.
- Cooling System: Marine engines generate a significant amount of heat, necessitating a cooling system to prevent overheating. This typically involves circulating water from the sea through the engine.
- Exhaust System: After combustion, exhaust gases need to be expelled from the engine. The exhaust system includes manifolds, turbochargers, and silencers to manage emissions and noise.
How Marine Diesel Engines Operate
The operation of a marine diesel engine can be broken down into several key stages:
- Intake: Fresh air is drawn into the cylinder as the piston moves down.
- Compression: The piston moves up, compressing the air to a high pressure and temperature, which prepares it for combustion.
- Injection: At the peak of the compression stroke, diesel fuel is injected into the cylinder. The high temperature of the compressed air ignites the fuel.
- Power Stroke: The rapid expansion of gases from combustion forces the piston down, generating power that turns the crankshaft.
- Exhaust: After the power stroke, the piston moves back up, pushing exhaust gases out of the cylinder through the exhaust valves.
This cycle repeats for each cylinder, providing continuous power to the vessel.
Advantages of Marine Diesel Engines
- Efficiency: Diesel engines are known for their fuel efficiency, making them ideal for long-distance marine travel.
- Durability: They are built to withstand harsh marine environments and operate for thousands of hours with proper maintenance.
- Torque: Marine diesel engines produce high torque at low RPMs, which is essential for maneuverability in challenging conditions.
- Safety: Diesel fuel is less flammable than gasoline, enhancing safety aboard vessels.
Maintenance and Care
Maintaining a marine diesel engine is crucial for ensuring its longevity and reliability. Regular maintenance tasks include:
- Oil Changes: Regular oil changes help keep the engine lubricated and reduce wear.
- Fuel System Checks: Inspecting and replacing filters ensures that clean fuel is delivered to the engine.
- Cooling System Maintenance: Regularly checking the cooling system prevents overheating and engine damage.
- Inspections: Regular inspections can catch potential issues before they become significant problems.
Conclusion
Marine diesel engines play a vital role in the maritime industry, powering everything from fishing boats to luxury yachts. Understanding how these engines work provides insight into their efficiency, durability, and importance in global trade and transportation. With proper maintenance and care, marine diesel engines can provide reliable performance for years, supporting the world’s fleets on the high seas. Whether you’re a mariner or just curious about the technology, appreciating the intricacies of marine diesel engines is essential for anyone interested in maritime activities.
